Inside Labs
Inside Labs
How Your Muscle Mass Affects Your Liver Health: Exploring the Link Between Sarcopenia and NAFLD
Update 23.03.2023
5 December 2022
How Your Muscle Mass Affects Your Liver Health: Exploring the Link Between Sarcopenia and NAFLD
What Science Says About the Relationship Between Muscle Loss and Fatty Liver
According to a recent academic article in Clinical and Molecular Hepatology, sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are two common health problems related to aging that are closely linked. Sarcopenia, the progressive and generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and/or function, and NAFLD, the accumulation of fat in the liver due to metabolic and lifestyle factors, share several pathogenetic mechanisms that implicate a bidirectional relationship between the two conditions.
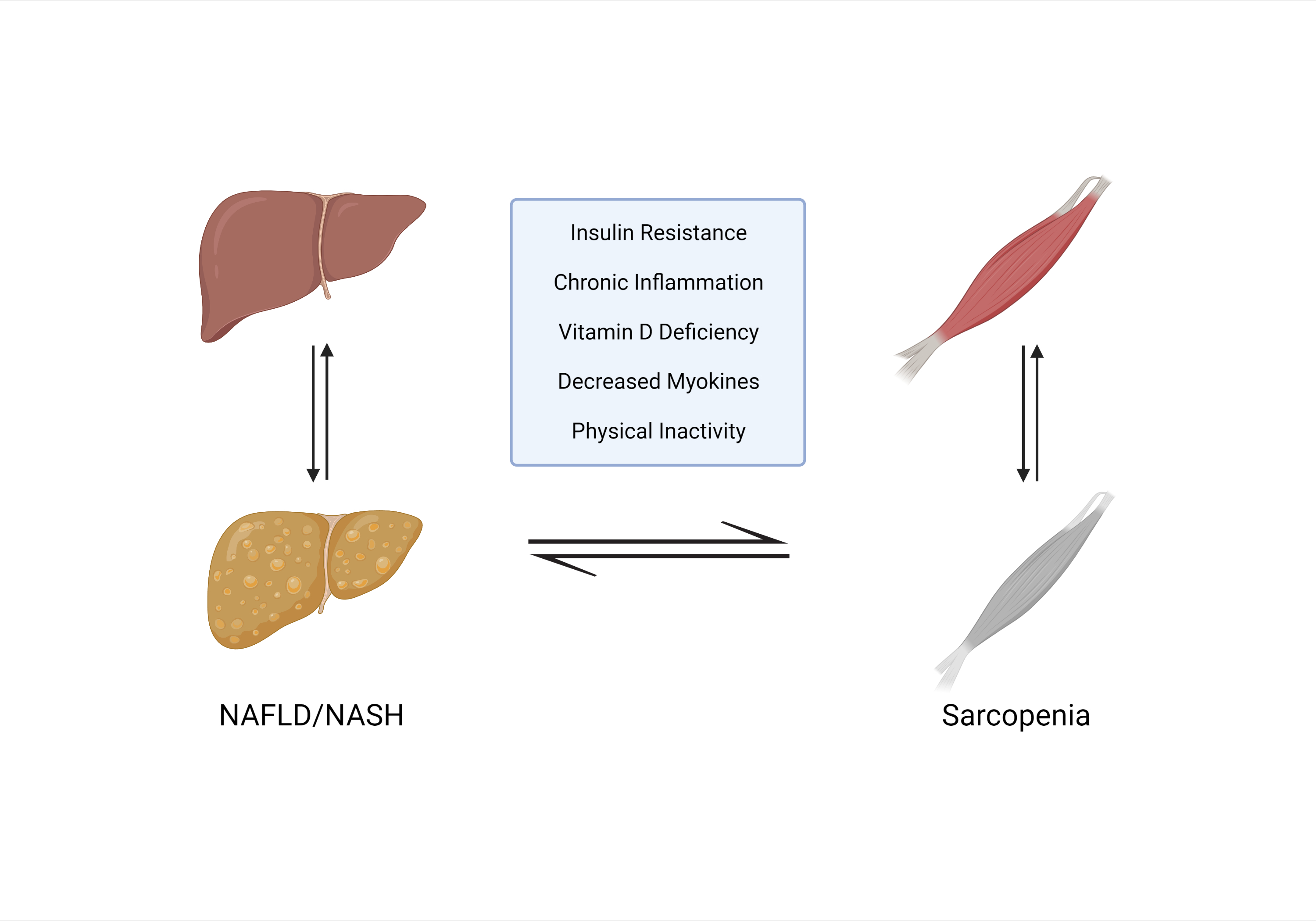
Figure 1. Bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Sarcopenia and NAFLD are becoming increasingly prevalent with the global epidemic of obesity and metabolic syndrome, and several studies have revealed their close link. Insulin resistance, hormonal imbalance, systemic inflammation, myostatin and adiponectin dysregulation, nutritional deficiencies, and physical inactivity are all common mechanisms that contribute to the development of both conditions.
Insulin resistance (IR) is the main pathologic mechanism causing both sarcopenia and NAFLD, resulting from the loss of skeletal muscle mass. This leads to the accumulation of triglycerides (TGs) in skeletal muscle and the liver, often referred to as ectopic fat. Inflammation and oxidative stress have also been linked to the pathogenesis of NAFLD.
However, there is currently not enough evidence to support a direct causal relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. It is still uncertain whether sarcopenia is a risk factor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or a consequence of NASH. Despite this, both conditions have been linked to advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, indicating that they are closely related.
It is important to note that the presence of low muscle strength is the primary parameter to suspect sarcopenia, while the presence of low muscle mass (quantity) and quality are confirmatory. Severe sarcopenia represents the coexistence of all these factors. Muscle quality also plays a critical role in the development of NASH, with myosteatosis being linked to muscle strength and function, as well as metabolic and liver-related clinical outcomes.
This review highlights the shared mechanisms and bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD, shedding light on the growing health concerns related to aging, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. While the direct causal relationship between these conditions is still unclear, their shared pathogenetic mechanisms demonstrate the need for a comprehensive approach to managing both conditions simultaneously.
In conclusion, the link between sarcopenia and NAFLD is not to be underestimated, and their shared pathogenetic mechanisms should be carefully considered by medical professionals when diagnosing and managing these conditions. Further research is necessary to fully understand the relationship between the two, but for now, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a well-balanced diet is a crucial step in preventing both sarcopenia and NAFLD.
Reference
* Author: Sae Kyung Joo, Won Kim
* Title: Interaction between Sarcopenia and NAFLD
* Journal: Clinical and Molecular Hepatology
* Published date: 2022 Dec 5
* DOI: https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2022.0358
Funding
This study was supported by the Research Program funded by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2022ER090200, Establishment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease cohort for prevention and management of cardiovascular disease).
About National Institute of Health in Korea
The Korea National Institute of Health (KNIH), one of the major operating components of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, leads the nation’s medical research. Over the past seven decades, the KNIH has made unwavering efforts to enhance the public’s health and innovate biomedical research. The KNIH seeks to eradicate diseases and make people healthier. The KNIH establishes a scientific basis and evidence underlying health policy as well as provides national research infrastructures. We also promote public health research. To this end, we make efforts to enrich a health research environment by granting funds to research projects and keeping our resources, data, and facilities more open and accessible to researchers.
Website: https://nih.go.kr/eng/main/main.do

